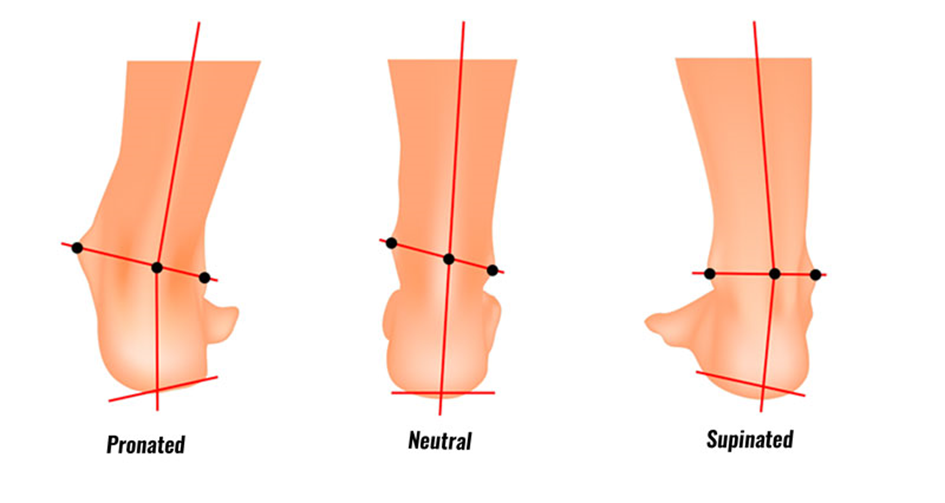
The difference between supination & pronation
Share
Supination and pronation refer to the orientation and mechanics of your hand, arm, or foot in an upward or downward direction.
When referring to your feet, supination and pronation involve the mechanics of your gait and how your weight is distributed as you walk or run.
Achieving proper weight distribution on your feet during movement is crucial for maintaining balance and preventing injury.
However, it's worth noting that understanding the complexities of supination and pronation in relation to the feet can be challenging, and it's important to seek guidance from a healthcare professional to properly identify any issues with your gait pattern.
Proper diagnosis and treatment can help prevent injuries and ensure optimal performance during physical activity.
1. Supination and Over-supination
1.1. Definition
Supination is a normal part of the gait cycle (walking/running). When your foot is in a supinated position, it is in a state of plantar flexion (toes pointed downwards), inversion (turning inward), and adduction (moving towards the midline of the body).
This combination of movements allows the foot to form a stable and rigid structure, providing a strong foundation for propulsion during the push-off phase of walking or running.
In other words, during the push-off phase, the foot must be able to transfer weight efficiently from the heel to the toes, allowing for a smooth and powerful stride.
Supination facilitates this transfer of weight by creating a stable base of support through the foot's rigid structure.
When the feet take this position in an exaggerated way is called over-supination. It means that when you walk, your weight tends to be more on the outside of your foot. Your shoe will show uneven wear on the outside part of the sole.
1.2.Causes
Over-supination is a biomechanical issue that can occur due to a variety of factors.
People with pes cavus or high arches are more likely to experience over-supination because their feet are naturally inclined to tilt outward.
Additionally, recurrent ankle sprains can weaken the lateral ankle ligaments, making the foot more prone to supination.
Lack of flexibility in the foot and ankle, as well as weakness in the anterior leg muscles (such as the tibialis anterior), can also contribute to over-supination. Individuals with certain neurological conditions, such as foot drop, can also be prone to over-supination because their muscles may not be able to provide adequate support for the foot.
1.3.Risk factors
Excessive supination can show up as a problem for runners, and other athletes, as the foot is less able to absorb shock.
Athletes with high arches are more prone to injuries such as shin splints, calluses, or bunions on the outer side of your foot, and pain in your heels and balls of your feet.
Additionally, people who supinate excessively, can have extra strain on their ankles.
1.4. Treatment
Therefore, it's important to identify and address any underlying factors contributing to over-supination to prevent these issues from occurring.
This may involve a combination of stretching (the calf muscles and the plantar fascia) and strengthening exercises, proper footwear selection, and orthotic devices to support the foot's arch and promote proper alignment.
2. Pronation and overpronation
2.1.Definition
The opposite of supination is pronation, which is another normal movement that occurs during the gait cycle (the sequence of events that occur during walking or running).
Pronation is the position of the foot when it combines dorsiflexion (lifting the foot upwards), eversion (turning outward), and abduction (moving away from the midline of the body).
Pronation is an important aspect of normal foot function because it allows the foot to adapt to different surfaces and absorb shock effectively.
During the initial contact phase of the gait cycle, the foot typically hits the ground in a slightly pronated position to help with shock absorption.
However, when the feet take this position in an exaggerated way is called over-pronation. It means that when you walk, your weight tends to be more on the inside of your foot and your arch tends to flatten out. Your shoe will show uneven wear on the inside part of the sole.
2.2.Causes
Excessive pronation, also known as overpronation, can result from various factors such as heredity, obesity, pregnancy, and repetitive impact on hard, flat surfaces.
This issue can develop due to the lack of flexibility in the foot or as a result of injury.
Many foot health experts suggest that the use of structured footwear in early childhood and exposure to consistently hard, flat surfaces in modern life may restrict the foot's range of motion and hinder the development of foot muscles, leading to overpronation in a majority of people in developed countries.
2.3.Risk factors
In the feet and ankles, over-pronation causes misalignment of the foot and ankle bones and excessive stretching of muscles, tendons and ligaments.
This is because the foot is not able to provide adequate support and stability during movement, resulting in excessive stress and strain on the foot and lower leg.
Therefore, over-pronation can increase the risk of several foot and lower leg problems such as flat feet, plantar fasciitis, and Achilles tendonitis.
It has also been associated with running injuries, knee pain, metatarsalgia, heel spurs, bunions, hammer toes, neuroma, hallux rigidus, bone spurs and posterior tibial tendonitis.
2.4. Treatment
For overpronation, physical therapy might be recommended. You will have help in strengthening your intrinsic muscles of the foot and calf muscles, and correct your foot alignment during gait or running.
Shoe insoles with higher heel cushioning are appropriate to correct feet posture throughout the day.
3. When to see a doctor
These foot postures may not be harmful or symptomatic. However, it can unconsciously alter your overall posture and/or increase the risk of injury, not only in the foot but also in your knees, hip, back and lower limb muscles.
It is important that you look for a medical opinion if you feel that it is getting worse or if it is conditioning your gait or even your daily functioning.
The doctor may recommend you to do some physical therapy for posture correction, strengthening and stretching your feet muscles or reeducating your gait/running pattern.
Most of the time, orthotics will be suggested, especially insoles, to promote more comfort and fix your alignment in your daily life without conscious correction. These insoles may need to be adapted to your feet, providing the perfect arch support and cushioning level for your needs.
If physical therapy and orthotics are not enough, surgery is an option to correct feet posture, especially in cases like pes equinus.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, the biomechanics of the foot are crucial in determining the alignment and function of the rest of the body.
Abnormal foot postures during gait can lead to pain and pathologies of the lower limbs.
Therefore, it's important to understand your foot type and gait pattern to identify any tendency towards overpronation or supination.
Proper footwear, such as stability or motion control shoes, can provide the necessary support and cushioning to maintain proper balance and weight distribution on your feet during physical activity or daily tasks.
By taking care of your feet, you can prevent injuries and improve your overall performance.
Author Bio
Inês Pinheiro
Certified Physiotherapist for Shoulder and Knee Injuries
Inês is a skilled physical therapist with a special interest and extensive experience in working with athletes, specifically football players and also neurologic patients.
References
- D, D. et al. (2018) “Reduction of foot overpronation to improve iliotibial band syndrome in runners: A case series,” Clinical Research on Foot & Ankle, 06(02). Available at: https://doi.org/10.4172/2329-910x.1000272.
- Chesak, J. (2018) How to keep your feet healthy: Tips, exercises, and more, Healthline. Healthline Media. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/tips-for-healthy-feet-footwear-hygiene (Accessed: April 3, 2023).
- Domínguez-Morales, M.J. et al. (2019) “Smart footwear insole for recognition of Foot pronation and supination using neural networks,” Applied Sciences, 9(19), p. 3970. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/app9193970.
- Overpronation (flat feet) - foot solutions (no date). Available at: http://www.footsolutions.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/OverpronationRev2.pdf (Accessed: April 3, 2023).
- Chat.openai.com (no date). Available at: https://chat.openai.com/ (Accessed: April 3, 2023).