Identifying Symptoms Of Bunions And Foot Distress
Share
In today's fast-paced world, where we rely heavily on our feet to keep up with our busy lives, it's crucial to pay attention to any signs of discomfort. Bunions and foot distress are common conditions that can affect anyone, causing pain and hindering mobility. Identifying the symptoms early on is vital for prompt treatment and preventing further complications. In this article, we will take a closer look at bunions, foot distress, and how to recognize their symptoms.
Understanding Bunions: An Overview
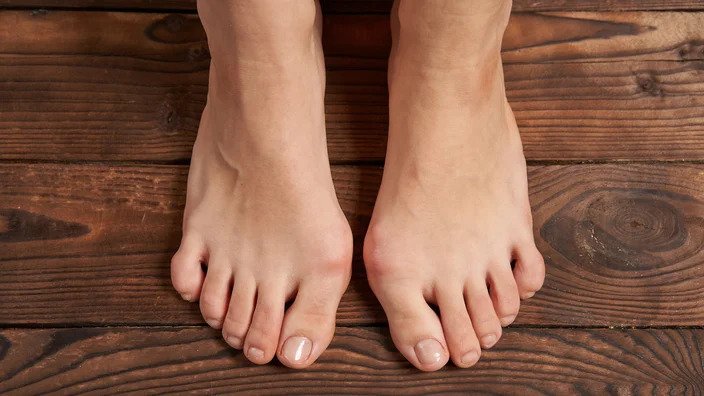
Bunions, also known as hallux valgus, are bony bumps that form at the base of the big toe. They occur when the joint at the base of the big toe becomes misaligned, causing the toe to point inward, towards the other toes. Over time, this misalignment leads to the formation of a bunion.

Bunions can be a source of discomfort and pain for many individuals. The pressure exerted on the joint can cause inflammation and swelling, making it difficult to walk or wear certain types of shoes. In severe cases, bunions can even lead to deformity of the foot.
Causes and Risk Factors of Bunions
While the exact cause of bunions is not fully understood, several factors contribute to their development. These factors may include:
Genetics: Certain foot structure traits can be inherited, making some individuals more prone to developing bunions. If you have a family history of bunions, you may have an increased risk of developing them yourself.
Footwear: Wearing tight, narrow shoes or high heels can put excessive pressure on the toes, increasing the risk of bunions. The constant compression and friction can gradually push the big toe out of alignment, leading to the formation of a bunion.
Joint disease: Certain conditions, such as arthritis, can weaken the structures around the toe joint, making bunion formation more likely. The inflammation and damage caused by arthritis can disrupt the normal alignment of the joint, contributing to the development of a bunion.
It is important to note that while these factors can increase the likelihood of developing bunions, they do not guarantee their occurrence. Some individuals with no known risk factors may still develop bunions, while others with multiple risk factors may never experience this condition.
It is also worth mentioning that bunions can affect people of all ages, although they are more commonly seen in adults. Women are more prone to developing bunions compared to men, which may be attributed to the higher prevalence of wearing tight-fitting shoes and high heels among women.
If you suspect that you have a bunion or are experiencing foot pain, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include conservative measures such as wearing wider shoes, using orthotic inserts, or in some cases, surgical intervention.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Bunions
Bunions are a common foot condition that can cause discomfort and pain. They typically develop gradually and worsen over time. Recognizing the early signs of bunions is crucial in seeking timely treatment and preventing further complications.
Early Signs to Look Out For
In the early stages, bunions may present with mild symptoms that can easily be overlooked. However, paying attention to these signs can make a significant difference in managing the condition. Some common early symptoms of bunions include:
Persistent pain or tenderness at the base of the big toe:
This is one of the primary indicators of a bunion. The pain may be dull or sharp and can vary in intensity and it’s located on the ball of the hallux.
Redness, swelling, or inflammation around the bunion:
As the bunion progresses, the affected area may become visibly red, swollen, or inflamed. This can cause discomfort and sensitivity.
Difficulty moving the affected toe:
Bunions can restrict the movement of the big toe, making it challenging to flex or extend it fully. This limitation can affect your overall mobility.
It's important to note that bunions can vary in severity and progress at different rates for each individual. Seeking medical advice at the earliest signs can help prevent further complications and alleviate discomfort.
Progression of Bunion Symptoms
If left untreated, bunions can cause increasingly severe symptoms that can significantly impact your daily life. These symptoms may include:
Chronic pain that persists throughout the day:
As the bunion progresses, the pain can become more constant and intense. It may affect your ability to walk or engage in physical activities.
Corns or calluses developing on or between the toes:
The pressure exerted by the bunion can lead to the formation of corns or calluses. These hardened areas of skin can be painful and may require additional treatment.
Restricted movement of the big toe or stiffness in the joint:
As the bunion worsens, the range of motion in the big toe may become limited. This can result in stiffness and difficulty performing activities that require toe mobility..
Deformity of the foot, with the big toe overlapping or crossing over the adjacent toes:
In severe cases, the bunion can cause the big toe to shift position, overlapping or crossing over the adjacent toes. This deformity can be visually noticeable and may affect shoe fit and comfort.
It's important to remember that bunions are progressive and can worsen over time if left untreated. Seeking professional medical advice and exploring treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Foot Distress: Beyond Bunions
Defining Foot Distress
While bunions are a common cause of foot distress, there are various other conditions that can contribute to discomfort and pain in the feet. Foot distress refers to any condition or injury that affects the normal function of the feet, causing pain, inflammation, or impaired mobility.

Foot distress can be a result of various factors, including improper footwear, overuse, trauma, or underlying medical conditions. It is important to understand that foot distress is not limited to a single condition, but rather encompasses a wide range of issues that can affect the feet.
When it comes to foot distress, it is crucial to seek proper medical attention and diagnosis. A healthcare professional specializing in podiatry can help identify the specific cause of foot distress and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Common Types of Foot Distress
Several common foot distress conditions include:
Plantar Fasciitis: Inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that supports the arch of the foot.
Plantar fasciitis is a common condition characterized by heel pain, especially in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest. It is often caused by repetitive strain or overuse of the plantar fascia, leading to micro-tears and inflammation. Treatment for plantar fasciitis may include rest, stretching exercises, orthotic devices, and in severe cases, surgery.
Morton's Neuroma: Thickening of the tissue around the nerves leading to the toes, often causing sharp, burning pain.
Morton's neuroma is a painful condition that affects the ball of the foot, usually between the third and fourth toes. It occurs when the tissue around the nerves thickens, causing irritation and compression. Common symptoms include a sharp, burning pain, tingling, or numbness in the affected area. Treatment options for Morton's neuroma may include footwear modifications, orthotic devices, corticosteroid injections, or in severe cases, surgery.
Achilles Tendonitis: Inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone.
Achilles tendonitis is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon, which runs down the back of the lower leg to the heel bone. It is often caused by overuse or repetitive strain on the tendon, leading to micro-tears and inflammation. Common symptoms include pain, swelling, and stiffness in the back of the ankle. Treatment for Achilles tendonitis may include rest, physical therapy, orthotic devices, anti-inflammatory medications, or in severe cases, surgery.
These are just a few examples of the many foot distress conditions that individuals may experience. It is important to remember that each person's foot distress may be unique, and treatment options may vary depending on the specific condition and individual needs.
Symptoms of Foot Distress
Pain and Discomfort: Initial Indicators
The most common symptom of foot distress is pain and discomfort in the affected area. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by tenderness, swelling, or redness. It's important to pay attention to any persistent pain or discomfort that limits your ability to walk or engage in everyday activities.
Physical Changes in Your Foot
In addition to pain, foot distress can cause physical changes in your foot's appearance or function. These changes may include:
- Swelling or inflammation around the affected area
- Visible deformities, such as misaligned toes or protrusions
- Difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot
The Connection Between Bunions and Foot Distress
How Bunions Contribute to Foot Distress
Bunions can significantly contribute to foot distress and exacerbate existing conditions. The misalignment of the big toe caused by bunions can place additional stress on the surrounding structures and alter the foot's biomechanics. This altered gait and pressure distribution can lead to the development or worsening of foot distress conditions and also developing knee, leg or hip pathologies.
Preventing Further Complications
Early identification and management of foot distress conditions, including bunions, are crucial for preventing further complications. Seeking professional medical advice and adopting preventive measures can help alleviate symptoms, reduce pain, and improve foot function.
Don't let bunions and foot distress hinder your mobility and quality of life. By understanding the symptoms and seeking early treatment, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining healthy and pain-free feet.
Author Bio

Marlene Carvalho
Certified Sports Physiotherapist of Elite and Olympic athletes; Performance Coach to racing drivers
Marlene Carvalho is a sports physiotherapist passionate about all things sports.






