Foot pain chart: Understanding your foot pain
Share
Understanding your foot pain plays a vital role in selecting the appropriate treatment for optimal relief. We've included a detailed foot chart highlighting various pain areas, enabling you to pinpoint the source of your discomfort.
As we explore each area, we will discuss potential causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options. Gaining a deeper understanding of foot pain is essential for making informed decisions about your foot health, leading to better outcomes and enhanced overall well-being.
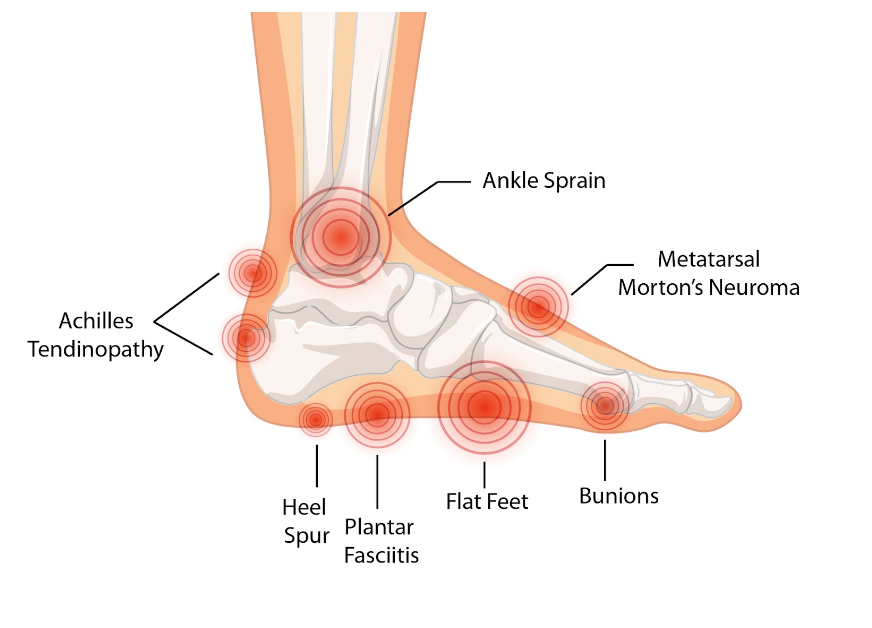
Foot pain chart

Discover how OrthoFlexx arch support insoles can ease your foot pain and provide lasting relief.
Plantar Fasciitis

Plantar Fasciitis is a condition that causes pain and inflammation in the plantar fascia, the thick tissue on the bottom of the foot. It's usually caused by overuse, particularly from activities such as running, jumping, or standing for extended periods.
The primary symptom of plantar fasciitis is pain on the bottom of the foot, particularly near the heel. This pain can be severe in the morning and may improve with activity but worsen as the day progresses.
Treatment often includes rest, ice, stretching exercises, and over-the-counter pain medications. Supportive shoes and insoles, night splints, physical therapy, and steroid injections may also be used in more severe cases.
If you want to learn more about Plantar Fasciitis, check out our exclusive post: Understanding Plantar Fasciitis and Its Pain Symptoms.
Achilles Tendinopathy

Achilles tendinopathy is a common injury that happens when the Achilles tendon is overused or submitted to excessive stress. Athletes are particularly susceptible to it, but it can also affect non-athletes, especially those who are overweight or who suddenly start or increase their physical activity.
Morning and post-exercise pain, swelling of the tendon, and functional impairment are the most common symptoms in an initial phase. Calf muscle fatigue and stiffness of the Achilles are also typical symptoms. If left untreated, the pain can become chronic.
To manage Achilles tendinopathy, start by adjusting activity intensity and frequency and gradually increasing the load on the tendon and calf muscles. Physical therapy can help manage other impairments and risk factors like foot misalignment or tendon stiffness. Orthotics like insoles and heel lifts can also be useful to improve alignment and reduce pressure on the tendon. In rare cases, more invasive interventions may be necessary.
To learn more about Achilles Tendinopathy, check out our post Sudden Foot Pain Without Injury.
Heel Spur

Heel or calcaneal spur is a bony growth that grows inside your foot between your heel and arch.
A heel spur may not produce symptoms, but when it does, people may experience severe pain that feels like a knife sticking into the bottom of their feet when standing up after rest or during weight-bearing activities. Inflammation and a bony protrusion at the front of the heel can also be symptoms.
If you have heel pain, rest and consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Treatment for heel spurs may involve cold packs, anti-inflammatory medication, physical therapy, stretching exercises, and changes in footwear, including night splints, insoles, or other shoe inserts for arch support and cushioning. Taping can be used to rest the muscles. Surgery is rarely necessary, as over 90% of patients recover with nonsurgical treatments.
Check out our exclusive post to learn the difference between heel spurs and plantar fasciitis.
Morton’s neuroma

Morton's neuroma, also called intermetatarsal neuritis, is a condition that can cause foot pain. It is a degenerative and compressive nerve condition that leads to fibrosis. It usually affects the third intermetatarsal space, followed by the second and then the fourth, but it can also affect multiple areas or occur in both feet.
The main symptoms are abnormal forefoot sensations, like burning or numbness in the toes, with no apparent trauma. Pain is felt in the forefoot, toes, and/or dorsal web space when putting weight on the foot, especially in the morning or with pressure. This can limit footwear choices and weight-bearing activities.
The treatment for Morton's neuroma can be non-surgical or invasive. Nonsurgical treatments include rest, ice, wearing wider toe boxes and low-heeled shoes, foot orthoses and metatarsal pads, physical therapy, extracorporeal shockwave therapy, and medication. If these treatments don't work, corticosteroid or sclerosing injections may be recommended. The final option is surgery.
Check out our exclusive post to learn more about Morton's Neuroma here.
Ankle Sprain

Ankle sprains are a common injury that occurs when the ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. The severity of an ankle sprain depends on the number of ligaments involved and the extent of the tear.
Symptoms of an ankle sprain can include pain, swelling, tenderness, bruising, and instability of the ankle.
Most ankle sprains can be treated with conservative methods, such as rest, ice, elevation, compression, medication, and immobilization with taping or bracing techniques. Physical therapy exercises may also be necessary to restore strength, range of motion, functional movement, and stability. However, if symptoms persist despite non-operative treatment, surgery may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the injured ligaments.
Learn more about prevention tips for foot and ankle injuries here.
Bunions - Hallux Valgus

A bunion, or Hallux Valgus, is a painful bony bump inside the foot near the big toe. Along with the visible bump, other common symptoms are tenderness, redness, inflammation, calluses, and stiffness in the toe. Poorly fitting shoes worsen the symptoms, and as the bunion worsens, walking can become difficult.
Although nonsurgical treatment cannot cure a bunion, it can effectively alleviate symptoms and prevent the bunion from progressing. Wearing wider shoes with adequate toe room, using padding and insoles, and other orthotic devices can relieve bunion pain and reduce pressure on the affected toe. However, if the pain persists and makes it difficult to walk, surgery may be necessary to correct the deformity.
Check out our exclusive post on how to shrink bunions naturally here.
Flat Feet - Pes Planus

The arch of your foot is the area between your heel and the ball. Flatfoot is when the arch falls and becomes closer than expected to the ground during weight-bearing.
Flat feet can cause pain in the midfoot, heel, lower leg, knee, hip, and back, and may also result in leg cramps. Uneven wear on shoes is a common issue for individuals with flat feet due to uneven weight distribution. This condition can also increase the likelihood of sprains, stress fractures, and fatigue. As flat feet progress, an altered gait pattern may develop, which can worsen symptoms.
The rehabilitation of pes planus aims to prevent further deterioration and alleviate pain. Physical therapy modalities, such as stretching and strength exercises for the foot, can be effective, along with patient education on proper footwear, the use of insoles or other orthotics to support the foot arch, and medication.
In cases where conservative treatment is ineffective, surgery may be necessary to correct the foot posture.
Check out our exclusive post on The best way to fix flat feet
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of foot pain and their potential causes is critical for selecting the right treatment and achieving optimal relief.
While we have covered some of the most common foot pain, it is important to remember that there are numerous other types of foot pain that were not discussed.
By taking the necessary steps to understand and address your foot discomfort, you can significantly improve your overall well-being and maintain good foot health.
Always consult with your doctor when experiencing pain to ensure you receive the appropriate care and treatment.
Discover how OrthoFlexx Arch Support Insoles can ease your foot pain and provide lasting relief.
Discover why over 45,000 people trust OrthoFlexx arch support insoles for lasting foot pain relief and superior support.
Author Bio

Inês Pinheiro
Certified Physiotherapist for Shoulder and Knee Injuries
Inês is a skilled physical therapist with a special interest and extensive experience in working with athletes, specifically football players and also neurologic patients.